Hamstring Strain
■ ■ ■ Description
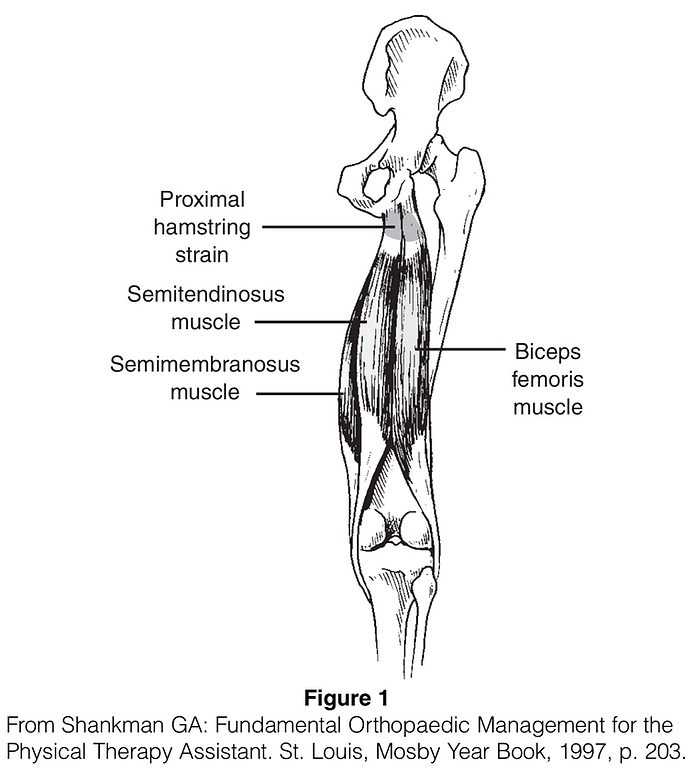
Hamstring strain is characterized by inflammation and pain in the back of the thigh along the hamstring muscles. There are three muscles that comprise the hamstring muscle group, going from the hip or upper thigh across the back of the knee to the leg. This structure is important for bending the knee, straightening the hip, and helping stabilize the knee. It is also important for running and jumping. These tendons feel like ropes in the back of the knee. This is the most common injury of the thigh.
Hamstring strains are usually grade 1 or 2 strains. A grade 1 strain is a mild strain. There is a slight pull without obvious tearing (it is microscopic tearing). There is no loss of strength, and the muscle-tendon unit is the correct length. A grade 2 strain is a moderate strain. There is tearing of fibers within the substance of the muscle or tendon or where the tendon meets the bone or muscle. The length of the muscle-tendon unit may be increased, and there is usually decreased strength. Agrade 3 strain is a complete rupture.
■ ■ ■ Common Signs and Symptoms
-
Pain, tenderness, swelling, warmth, or redness over the hamstring muscles at the back of the thigh
-
Pain that worsens during and after strenuous activity
-
“Pop” often heard in the area at the time of injury
-
Muscle spasm in the back of the thigh
-
Pain or weakness with running, jumping, or bending the knee against resistance
-
Crepitation (a crackling sound) when the tendon is moved or touched
-
Bruising in the thigh 48 hours following the injury
-
Loss of fullness of the muscle or area of muscle bulging with complete rupture
■ ■ ■ Causes
-
Strain from overuse or sudden increase in amount or intensity of activity
-
Single violent blow or force to the back of the knee or the hamstring area of the thigh
■ ■ ■ Risk Increases With
-
Sports that require quick starts (sprinting or running races and other track events (racquetball, badminton)
-
Sports that require jumping (basketball and volleyball)
-
Kicking sports and waterskiing
-
Contact sports (soccer or football)
-
Poor physical conditioning (strength and flexibility), including muscle imbalance
-
Inadequate warm-up before practice or play
-
Previous thigh, knee, or pelvis injury
-
Poor technique
-
Poor posture
■ ■ ■ Preventive Measures
-
Appropriately warm up and stretch before practice or competition.
-
Maintain appropriate conditioning:
-
Cardiovascular fitness
-
Thigh and hip flexibility
-
Muscle strength and endurance
-
-
Use proper technique and posture.
-
Wear proper protective equipment (knee or thigh pads).
■ ■ ■ Expected Outcome
This condition is usually curable within 2 to 6 weeks if treated appropriately.
■ ■ ■ Possible Complications
-
Prolonged healing time if not appropriately treated or if not given adequate time to heal
-
Chronically inflamed tendon, causing persistent pain with activity that may progress to constant pain
-
Recurrence of symptoms if activity is resumed too soon
-
Proneness to repeated injury (in up to 25% of cases)
■ ■ ■ General Treatment Considerations
Initial treatment consists of medication and ice to relieve the pain, stretching and strengthening exercises (primarily straightening the knee), and modification of the activity that initially caused the problem. These all can be carried out at home, although referral to an athletic trainer or physical therapist for further evaluation and treatment may be helpful. An elastic bandage or neoprene (made of swimsuit-like material) sleeve may help reduce swelling and keep the muscles warm, alleviating symptoms. Crutches may be recommended, if the strain is severe and the athlete is limping, until the pain and inflammation settle down, usually for the first 24 to 72 hours. Surgery is necessary to reattach muscle-tendon if it pulls off bone (uncommon). Suturing or sewing torn muscle is usually not successful.
■ ■ ■ Medication
-
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications, such as aspirin and ibuprofen (do not take for the first 3 days after injury or within 7 days before surgery), or other minor pain relievers, such as acetaminophen, are often recommended. Take these as directed. Contact your physician immediately if any bleeding, stomach upset, or signs of an allergic reaction occur.
-
Topical ointments may be of benefit.
-
Pain relievers may be prescribed as necessary by your physician. Use only as directed.
-
Injections of corticosteroids may be given to reduce inflammation, although not usually for acute injuries.
■ ■ ■ Heat and Cold
-
Cold is used to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. Cold should be applied for 10 to 15 minutes every 2 to 3 hours for inflammation and pain and immediately after any activity that aggravates your symptoms. Use ice packs or an ice massage.
-
Heat may be used before performing stretching and strengthening activities prescribed by your physician, physical therapist, or athletic trainer. Use a heat pack or a warm soak.
■ ■ ■ Notify Our Office If
-
Symptoms get worse or do not improve in 2 weeks despite treatment
-
New, unexplained symptoms develop (drugs used in treatment may produce side effects)
View as PDF